Admin
Users & Call Controls
- Creating Extensions for Users
- Editing and Managing Extensions
- Creating Teams & Assigning Extensions
- Configuring Agent Status & BLF
- Managing Extension Schedules
- Managing User Roles
- Managing Call Controls
- Setting up Shared Parking
- Voicemails
- The BLF Function
- Configuring the Speed Dial
- Configuring the Busy Lamp Field (BLF)
Deployment Methods & System Requirements
Installation Guides
RingQ FQDNs
RingQ FQDNs
How they work in Single Tenant (ST) and Multi-Tenant (MT) deployments
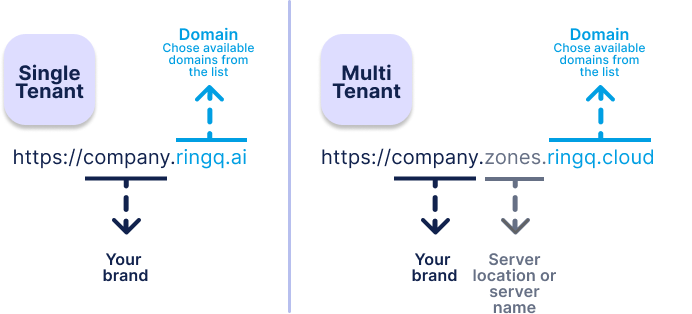
1. Single-Tenant (ST) FQDN
FQDN Format:
How it works:
- A dedicated environment for each customer/company.
- All backend services, databases, and configurations are isolated.
- The domain (FQDN) is clean and customer branded.
- Often hosted under a dedicated cloud project or virtual machine group.
Use Cases:
- Enterprises needing higher data isolation and security.
- Custom deployment, branding, and feature control.
2. Multi-Tenant (MT) FQDN
FQDN Format:
How it works:
- Multiple tenants (companies/users) share the same infrastructure.
- Logical isolation via namespaces, org IDs, or tenant IDs.
- The FQDN includes the company name and server zone (e.g., us-east, eu-west), allowing routing to the correct environment.
Use Cases:
- SaaS product model.
- Fast onboarding, cost-effective for small to medium clients.
- Centralized updates and shared resource pools.
FQDN Examples:
| Type | FQDN Example | Infra Type | Isolation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST | https://acmecorp.ringq.ai | Dedicated VM/cluster | High (per-customer) |
| MT | https://acmecorp.useast1.ringq.cloud | Shared SaaS infra | Medium (logical) |
Depending on your company’s needs, you can choose which option suits you best:
| Need | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Customization & Branding | Single Tenant |
| Lower cost & fast rollout | Multi-Tenant |
| Regulatory Compliance | Single-Tenant |
| Scale with multiple users | Multi-Tenant |
